Resilient Growth Amid Global Uncertainties
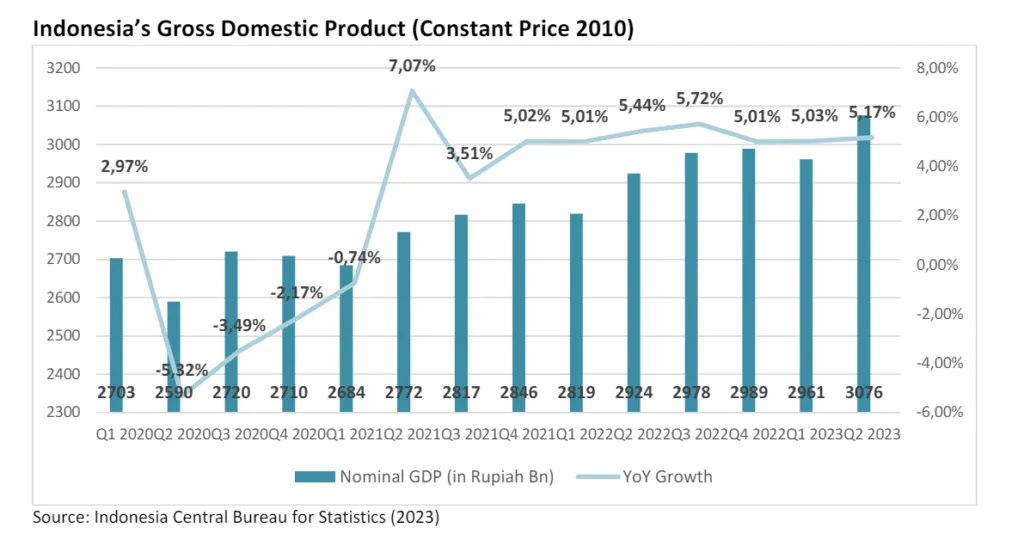
Indonesia’s 2024 economic outlook is defined by domestic strength and external challenges. Over the past five years, the country’s GDP has shown resilience, consistently growing around 5%, despite global disruptions from COVID-19. This growth is driven primarily by robust domestic consumption, supported by a burgeoning middle class with rising disposable incomes. For those seeking a thorough market research Indonesia, this article provides an insightful analysis of the country’s 2024 economic outlook.
Domestic spending on essential goods and services has provided a strong buffer against external headwinds. Additionally, Indonesia’s manufacturing sector is witnessing a resurgence, driven by government policies promoting foreign investment and value-added processing of natural resources. This diversification beyond traditional commodity exports has further bolstered economic growth.
Key Drivers and Potential Roadblocks
Investment in infrastructure, energy, and digital sectors is on the rise, translating into enhanced productivity, job creation, and long-term economic dynamism. However, external threats such as global trade slowdowns, rising commodity prices, and geopolitical tensions could impact exports and investment flows. Prudent economic policies and continued diversification efforts will be crucial in navigating these volatile winds.
Despite positive trends, infrastructure shortcomings, bureaucratic hurdles, and skills gaps could impede economic activity. Addressing these bottlenecks through targeted reforms and investments is essential to unlock further growth potential. Moreover, while GDP growth remains encouraging, addressing income inequality and fostering inclusive growth are imperative. Policies aimed at improving access to education, healthcare, and financial services for disadvantaged groups will be crucial for widespread prosperity.
Inflation and Monetary Policy
Indonesia’s inflation rate, influenced by global and domestic pressures, remains within the target range set by Bank Indonesia. Factors such as global commodity price hikes, supply chain disruptions, and rebounding domestic demand post-pandemic have contributed to inflationary pressures. While the government has taken steps to reduce fuel subsidies for fiscal sustainability, this has led to temporary inflation spikes.
Bank Indonesia has responded with gradual interest rate increases to curb aggregate demand without stifling economic growth. Targeted interventions, such as price controls on essential goods and fuel subsidies for specific groups, aim to mitigate the impact on vulnerable populations. Despite current inflationary pressures, a decline is expected in 2024 due to softening global commodity prices and normalized domestic demand growth.
Employment and Labor Market Challenges
While Indonesia’s official unemployment rate has gradually decreased to around 5%, underemployment remains a significant concern. Many individuals are in jobs below their skill levels or working fewer hours than desired, masking the true extent of labor market challenges. The informal economy, contributing significantly to economic activity, often presents precarious employment conditions without social security or benefits.
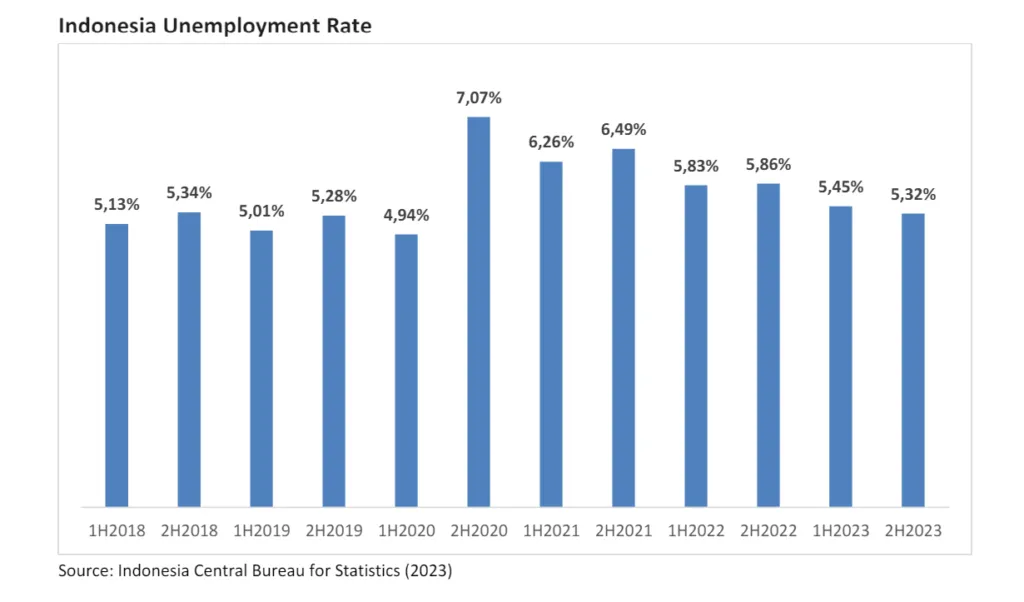
Bridging the skills gap through targeted training programs and vocational education is crucial to improve employability. Indonesia’s young and expanding population creates a large pool of job seekers, which could potentially outpace job creation if adequate economic opportunities are not generated. Additionally, global economic slowdowns, trade disruptions, and volatile commodity prices could impact export-oriented industries, leading to job losses.
Future Prospects and Strategic Initiatives
The Presidential Election in 2024 adds another layer of uncertainty to Indonesia’s economic landscape. Potential increases in fiscal spending during the campaign period could provide a short-term boost, but concerns about fiscal sustainability and long-term debt implications remain. The policy direction of the next administration will be pivotal in shaping the country’s economic trajectory. Investors will closely watch candidates’ stances on infrastructure development, industrial diversification, and fiscal responsibility.
Despite these uncertainties, Indonesia’s large and increasingly affluent middle class provides a robust domestic market, insulating the economy from external shocks. The country’s wealth of natural resources offers opportunities for value-added processing, export diversification, and attracting foreign investment. A young and skilled workforce has the potential to drive long-term productivity and innovation, supporting sustained economic growth.
In summary, the Indonesia economic outlook for 2024 hinges on leveraging domestic strengths while navigating external uncertainties. Maintaining macroeconomic stability through prudent fiscal and monetary policies, addressing structural inequalities, and investing in human capital and economic diversification will be key to ensuring sustainable and inclusive growth. Effective policy choices post-election can set the stage for a future of high-growth development, making Indonesia a beacon of economic resilience and opportunity in Southeast Asia.
For detailed insights and strategic directions, consider consulting with the experts in our Market Research Indonesia team at Eurogroup Consulting to stay ahead of these evolving trends.